How to Use Mind Mapping to Plot Your Next Big Idea offers a powerful approach to structuring thoughts and enhancing creativity through visual organization. Mind mapping, a technique rooted in cognitive science, serves as a tool to facilitate brainstorming, allowing individuals to unlock their potential and explore innovative ideas. The evolution of this technique has seen it embraced by successful figures across various fields, showcasing its effectiveness in transforming concepts into actionable plans.
This method not only provides cognitive benefits but also fosters an environment of creativity and organization, making it an invaluable asset for anyone looking to refine their ideas. Through this guide, we will delve into the myriad of ways mind mapping can be employed to enhance the ideation process, from utilizing basic tools to advanced strategies that elevate the effectiveness of your brainstorming sessions.
Introduction to Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is a visual tool that organizes information, enhancing brainstorming and creativity. This technique allows individuals to capture thoughts, ideas, and concepts in a structured manner, often utilizing branches to represent relationships among various elements. By visually laying out ideas, users can easily identify connections, prioritize tasks, and stimulate innovative thinking.The concept of mind mapping has evolved over decades, with its roots tracing back to ancient civilizations that used diagrammatic representations to organize knowledge.
The modern iteration was popularized by Tony Buzan in the 1970s, who introduced a structured approach to mind mapping that incorporated colors, images, and s to facilitate learning and memory retention. Buzan’s contributions have been pivotal, leading to the widespread adoption of mind mapping across various fields, including education, business, and personal development.
Examples of Successful Mind Mapping Applications
Numerous successful individuals and projects have leveraged mind mapping to enhance their creative processes and achieve remarkable results. This technique has been particularly beneficial in brainstorming sessions, project planning, and strategic thinking. Notable examples include:
- J.K. Rowling utilized mind mapping to develop the intricate narrative of the “Harry Potter” series, allowing her to visualize character relationships and plot developments, which contributed to the series’ depth and coherence.
- Apple Inc. has employed mind mapping to fuel innovation and product development. The company’s brainstorming sessions often incorporate mind maps to explore new ideas and refine existing concepts, ensuring a robust pipeline of creative solutions.
- Albert Einstein is often cited as having used mind maps to explore complex theories and ideas, allowing him to connect disparate concepts and formulate groundbreaking scientific insights.
These examples illustrate the effectiveness of mind mapping as a powerful tool for organizing thoughts and fostering creativity across various domains.
Benefits of Mind Mapping for Idea Development
Mind mapping serves as an innovative tool for enhancing idea development by visualizing complex information in an organized manner. This technique harnesses the brain’s natural ability to connect concepts, facilitating a deeper understanding and retention of ideas. By employing mind mapping, individuals can navigate the intricacies of their thought processes while simultaneously unlocking their creative potential.The cognitive benefits of mind mapping are profound.
This method taps into how our brains work, leveraging visual-spatial reasoning to simplify information. Mind mapping engages both hemispheres of the brain, promoting a balance between analytical and creative thinking. This dual engagement leads to improved memory retention and recall, as the visual layout allows for easier navigation of ideas. The structure of a mind map, with its central idea branching out into s, mirrors the way our brains naturally categorize thoughts, providing a more intuitive approach to organizing information.
Cognitive Benefits of Mind Mapping
Utilizing mind mapping stimulates various cognitive functions that contribute to more effective idea development. The following points illustrate the key cognitive benefits:
- Enhanced Memory Retention: Visualizing information through mind maps helps individuals remember concepts more effectively, as the brain processes images faster than text.
- Improved Focus: Mind mapping encourages focused thinking by breaking down information into smaller, manageable sections, which can reduce overwhelm and increase clarity.
- Better Problem-Solving Skills: By visually mapping out problems and potential solutions, individuals can see connections between ideas that may not be immediately apparent, leading to more innovative solutions.
- Increased Engagement: The dynamic nature of mind mapping keeps individuals engaged, allowing for a more active participation in the idea development process.
Creativity and Organization of Thoughts
Mind mapping significantly enhances creativity by allowing individuals to explore ideas in a free-flowing manner. The visual nature of a mind map encourages brainstorming by providing a space to write down thoughts without judgment. This organic approach fosters an environment where spontaneous ideas can emerge.Moreover, mind mapping aids in organizing thoughts in a logical structure. Each branch of a mind map represents a related concept, enabling users to see the relationships among different ideas.
This organization is particularly beneficial during the initial phases of project planning or content creation, where a clear overview of all components is essential.
Real-World Scenarios of Mind Mapping Success
Numerous organizations and individuals have successfully implemented mind mapping to enhance their idea generation processes. Some notable examples include:
- Corporate Strategy Meetings: Companies like IBM utilize mind mapping during brainstorming sessions to visualize strategic goals and foster collaborative discussions among teams, resulting in more innovative product development.
- Education: Educators encourage students to use mind maps for organizing research projects, leading to improved clarity and focus, ultimately resulting in higher quality academic work.
- Personal Development Workshops: Facilitators often employ mind mapping techniques during coaching sessions to help clients articulate their goals, clarify their visions, and devise actionable plans.
Tools and Techniques for Mind Mapping
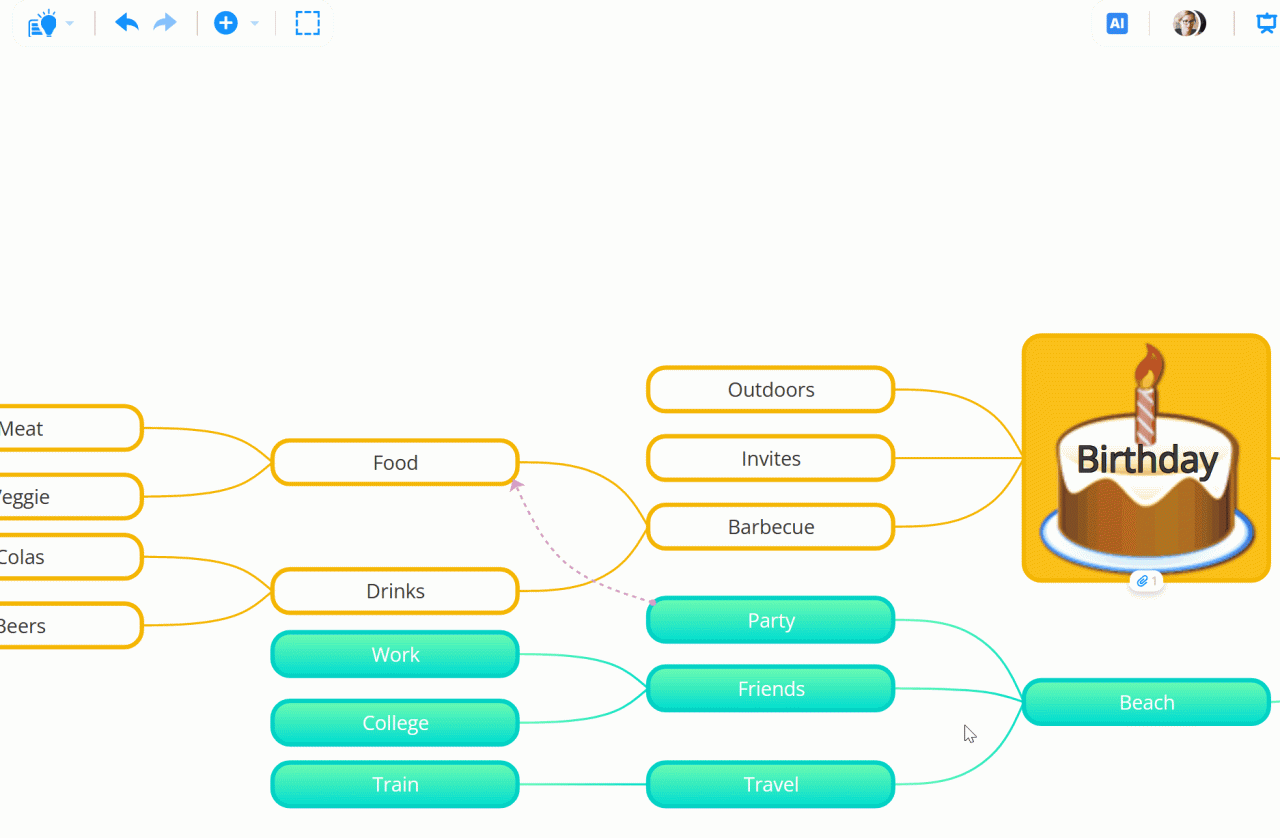
Mind mapping is an effective way to organize thoughts and visualize ideas, and utilizing the right tools can streamline this process. A variety of both software programs and physical materials are available to assist in creating mind maps, each offering unique features and advantages. Understanding these tools, as well as the various techniques for mind mapping, can enhance your creativity and productivity.
Available Tools for Creating Mind Maps
There are numerous tools available for mind mapping, ranging from digital software to traditional paper-based methods. The choice of tool often depends on personal preference, project requirements, and the intended audience. Here are some widely used options:
- Digital Software:
- XMind: A versatile mind mapping software that supports various diagram types and offers cloud storage for easy access.
- MindMeister: A collaborative online tool that allows multiple users to create and edit mind maps in real-time.
- Lucidchart: An intuitive diagramming tool that integrates mind mapping with flowchart capabilities, making it suitable for complex projects.
- Miro: A virtual whiteboard platform that provides mind mapping features alongside other brainstorming tools.
- Physical Tools:
- Whiteboards: Perfect for group brainstorming sessions, allowing for quick edits and visual representation of ideas.
- Sticky Notes: Great for jotting down individual ideas that can be easily rearranged as you develop your mind map.
- Pens and Markers: Using colored pens can help differentiate between topics and s, making the mind map more visually appealing.
- Large Paper Sheets: Ideal for creating extensive mind maps, allowing for spacious layouts and detailed illustrations.
Step-by-Step Process of Creating a Mind Map Using XMind
XMind is a powerful tool for creating structured mind maps. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use it effectively:
1. Download and Install XMind
Visit the official XMind website and download the software. Follow the installation instructions to set it up on your device.
2. Open a New Document
Launch XMind and create a new document. You will be presented with a blank canvas for your mind map.
3. Add the Central Idea
Click on the central node and type in your main idea or topic. This will serve as the anchor for your mind map.
4. Create s
Select the central node and use the shortcut (Tab key) to create sub-nodes. Enter relevant s that branch out from the main idea.
5. Further Break Down Ideas
For each , you can create additional branches using the same method. This allows for a hierarchical structure of ideas.
6. Customize Appearance
Utilize XMind’s formatting options to change colors, shapes, and fonts. This enhances clarity and visual appeal.
7. Save and Export
Once completed, save your mind map. XMind offers various export formats, including PDF and image files, for easy sharing.
Comparison of Mind Mapping Techniques
Different techniques for mind mapping cater to various organizational needs and personal styles. Here are three prominent methods:
- Radial Method:
The radial method starts with a central concept, branching outwards like spokes on a wheel. This technique is effective for showcasing relationships between ideas. - Tree Method:
In the tree method, the main idea sits at the top, with branches representing s leading downward. This hierarchical structure is useful for outlining topics with clear parent-child relationships. - Flowchart Method:
The flowchart method emphasizes the flow of ideas, often incorporating arrows and directional cues. This technique is beneficial for processes that involve sequential steps or decision points.
Each of these techniques offers different advantages depending on the complexity of the project and the individual’s preferences, providing flexibility in how ideas are organized and communicated.
Steps to Plot Your Next Big Idea Using Mind Mapping
Engaging in a mind mapping session can significantly enhance the clarity and depth of your ideas. By following a structured approach, individuals can organize their thoughts effectively and cultivate creativity, which is essential for developing impactful projects. This section will provide a clear framework for initiating a mind mapping session, complete with an example focused on a relevant theme.A structured approach to mind mapping involves several key steps that guide the ideation process.
Each step contributes to the development of a comprehensive mind map that encapsulates the core elements of your big idea. The following table Artikels these steps in an organized manner for easy reference.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Define Your Central Idea | Begin by identifying the main theme or project that you want to explore. This serves as the focal point of your mind map. |
| 2. Branch Out Key Concepts | From the central idea, create branches representing major s or components related to your main theme. |
| 3. Add Supporting Details | For each , include supporting ideas, facts, or concepts that elaborate on the branches. |
| 4. Use Visual Elements | Incorporate colors, images, and symbols to enhance memory retention and engagement with the mind map. |
| 5. Review and Refine | After completing the initial mind map, review its structure and content. Make necessary adjustments to improve clarity and organization. |
Detailed Example of a Mind Map: Launching a Sustainable Product
To illustrate the mind mapping process, consider the theme of launching a sustainable product. The following elements could be included in the mind map, each branching from the central idea:
Central Idea
Launching a Sustainable Product
Market Research
Trends in sustainability
Target audience analysis
Competitor evaluation
Product Development
Materials sourcing
Eco-friendly manufacturing processes
Design considerations
Marketing Strategies
Social media campaigns
Collaborations with eco-influencers
Educational content about sustainability
Sales Channels
E-commerce platforms
Local retailers
Partnerships with eco-friendly stores
In this example, the main theme is clearly defined, and each subsequent branch illustrates vital aspects of the product launch. Using visual elements such as color coding for different subcategories or icons representing various marketing strategies can further enhance the map’s effectiveness.By following these structured steps, you can effectively plot your next big idea using mind mapping techniques, ensuring a thorough exploration of the project at hand.
Advanced Mind Mapping Strategies
Advanced mind mapping strategies enhance creativity and structure in idea development by integrating various brainstorming techniques, emphasizing categorization and prioritization, and utilizing complex mind maps.Integrating mind mapping with other brainstorming techniques can significantly elevate the output of your ideation sessions. Techniques such as free writing, the SCAMPER method (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse), and the Six Thinking Hats method can all complement mind mapping.
By starting with a mind map, you can identify key themes and then use free writing to explore those themes in more depth. Additionally, applying the SCAMPER technique on a specific node of the mind map can lead to innovative solutions or new ideas that branch off your original concept.
Importance of Categorization and Prioritization
Categorization and prioritization are essential components of effective mind mapping. They enable the organizer to visually separate and rank ideas, making it easier to navigate through complex information. This structured approach allows for clear pathways to develop thoughts systematically.When categorizing ideas within a mind map, it is beneficial to use color coding or shape differentiation. For instance, major themes can be represented in bold colors while subcategories may be in lighter shades.
Moreover, prioritization can be achieved by numbering or labeling ideas based on importance or urgency. The following methods exemplify effective categorization and prioritization strategies:
- Use of Color Coding: Assign different colors to various categories, which not only enhances visual appeal but also aids in quicker recognition of themes.
- Hierarchical Structure: Organize ideas by tiers, where primary concepts branch off into secondary and tertiary sub-ideas, clarifying relationships and importance.
- Numeric Ranking: Implement a system to rank ideas based on feasibility or impact, allowing for focused development on the most promising concepts.
Examples of Complex Mind Maps
Complex mind maps can showcase the integration of advanced strategies, especially for multifaceted projects or ideas. One such example is a mind map designed for a product development project. This map could begin with the central idea of the product and branch out into various categories such as market research, design features, marketing strategies, and potential challenges. Within each category, specific elements can further branch off:
- Market Research may include target demographics, competitor analysis, and pricing strategies.
- Design Features could detail innovations, materials, user feedback, and aesthetic considerations.
- Marketing Strategies can encompass digital advertising, influencer partnerships, and promotional events.
- Potential Challenges would address supply chain issues, regulatory requirements, and customer acceptance.
Another complex example is a strategic planning mind map for a nonprofit organization. Here, the central node might symbolize the mission statement, with branches for programs, funding sources, community outreach, and partnerships. Each branch could delineate specific programs under the programs category, restrictions and opportunities under funding sources, and targeted community initiatives under outreach.By using advanced mind mapping strategies, individuals and teams can harness the power of visualization, categorize effectively, and prioritize their ideas to develop robust and actionable plans for their next big idea.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Mind Mapping
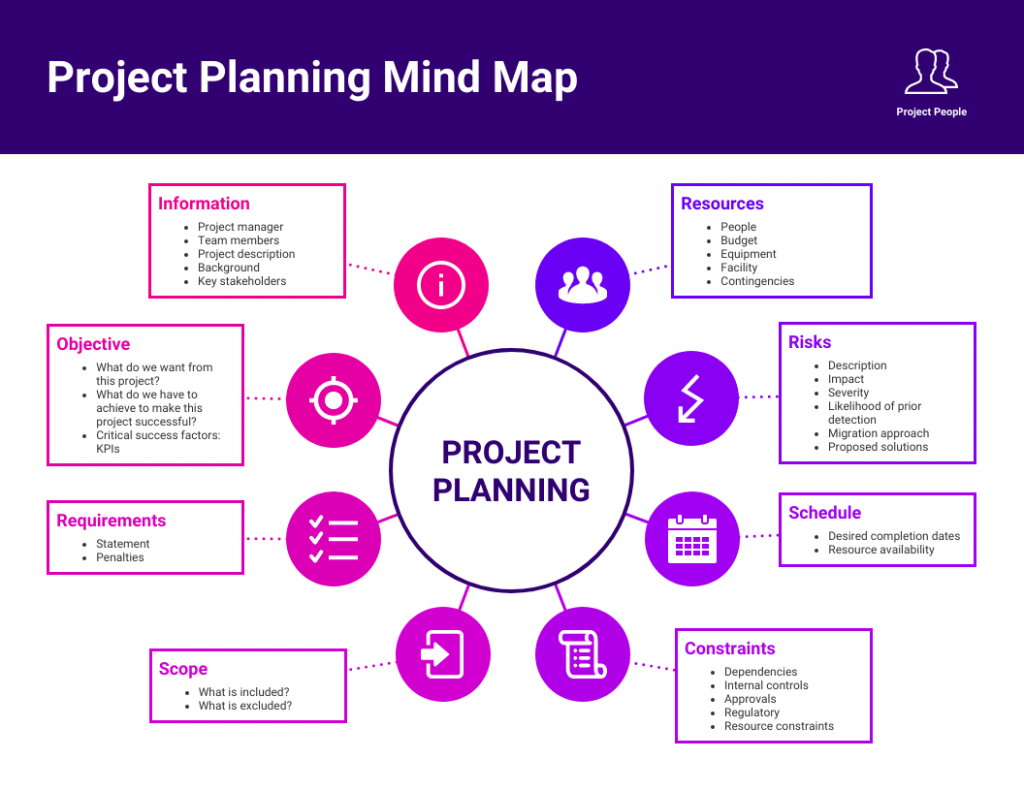
Creating an effective mind map requires careful consideration and attention to detail. While mind mapping can be a powerful tool for idea development, there are common pitfalls that individuals often encounter, which can hinder the clarity and effectiveness of their maps. Avoiding these mistakes is crucial to maximize the potential of mind mapping as a technique for organizing thoughts and generating innovative ideas.One common mistake is overcrowding the mind map with too much information, leading to cluttered visuals that can confuse rather than clarify.
Additionally, using vague labels and branching phrases can detract from the overall purpose of the mind map, making it difficult for the user to follow the intended flow of ideas. Maintaining clarity and organization is vital; therefore, it is essential to implement effective strategies to ensure that mind maps serve their purpose without ambiguity.
Frequent Mistakes in Mind Mapping
Understanding the frequent mistakes made in mind mapping can greatly enhance its effectiveness. Key pitfalls include:
- Overloading with Information: Including excessive details can lead to confusion. Each branch should focus on key concepts rather than exhaustive descriptions.
- Poorly Defined Branches: Using vague or non-descriptive labels can result in a lack of clarity regarding the connections between ideas.
- Lack of Structure: Failing to create a logical hierarchy can make it difficult to see the relationships between ideas. A well-structured mind map should have a clear main idea, with s logically branching out.
- Ignoring Visual Elements: Not utilizing colors, shapes, or images can make a mind map less engaging and harder to understand. Visual elements can enhance memory retention and comprehension.
- Neglecting to Review: Not revisiting and refining the mind map can leave it stagnant and ineffective. Regularly updating the map ensures its relevance and usefulness.
Maintaining Clarity and Organization
To enhance clarity and organization within mind maps, consider the following strategies:
- Limit Branching: Aim to keep each branch to a single or a short phrase. This helps maintain focus and prevents information overload.
- Utilize Color Coding: Implement color schemes to categorize different themes or topics. This visual aid can help in quickly identifying related sections.
- Consistent Formatting: Use a uniform style for text sizes and fonts to create a cohesive look. Consistency aids comprehension and retention.
- Incorporate Images and Icons: Including relevant images or icons can provide visual stimulus and reinforce ideas, enhancing memory recall.
- Regularly Update the Map: Reassess and revise your mind map periodically to reflect new insights or changes in the thought process, keeping it dynamic and effective.
Effective Versus Ineffective Mind Maps
The distinction between effective and ineffective mind maps is crucial for maximizing their utility. Effective mind maps are characterized by a clear focus, logical structure, and engaging visual elements, while ineffective maps often lack clarity and coherence. An effective mind map typically:
- Has a central theme that is easily identifiable.
- Utilizes branches that flow logically from the central idea.
- Incorporates visuals and color coding for easier understanding.
- Is concise, with each branch limited to essential information.
In contrast, an ineffective mind map may:
- Be cluttered with excessive information, making it difficult to follow.
- Have vague labels that do not clearly communicate the idea.
- Lack visual appeal, resulting in a dull representation of thoughts.
- Be poorly structured, leading to confusion about how ideas relate to one another.
“An effective mind map acts as a roadmap for your thoughts, guiding you toward clarity and innovation.”
Real-life Applications of Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is not only a theoretical concept; it has practical applications across various industries and professions. This versatile tool empowers individuals and teams to visualize complex information, enabling clearer thinking and enhanced creativity. By employing mind mapping techniques, professionals can streamline their workflows, generate innovative ideas, and effectively communicate their thoughts.Many industries benefit from mind mapping, including education, business, healthcare, and creative fields.
For instance, educators utilize mind mapping to promote active learning and facilitate lesson planning. In business, teams leverage mind mapping for project management, brainstorming sessions, and strategic planning. The healthcare sector employs mind mapping to track patient care processes and improve communication among medical staff.
Case Studies and Testimonials
Several case studies and testimonials illustrate the transformative impact of mind mapping on idea development. For example, a software development team at a tech startup utilized mind mapping to streamline their agile processes. By visualizing their project tasks and dependencies, they improved collaboration and reduced project delivery time by 30%.Another case study involves an author who used mind mapping to Artikel her novel.
The visual representation of character relationships, plot arcs, and themes allowed her to organize her thoughts coherently, leading to a completed manuscript ahead of schedule.
Specific Applications of Mind Mapping
Mind mapping serves a broad range of applications in daily life and business contexts. Understanding these applications can inspire you to incorporate mind mapping into your own routines. Here is a list of specific ways mind mapping can be utilized:
- Brainstorming Sessions: Teams can generate ideas visually, fostering creativity and collaboration.
- Project Management: Mind mapping helps track tasks, deadlines, and project milestones efficiently.
- Note-taking: Students can organize lecture notes or study materials in a visually engaging manner.
- Problem Solving: Mind maps facilitate the breakdown of complex problems into manageable components.
- Event Planning: Organizers can Artikel ideas, schedules, and logistics in a structured format.
- Strategic Planning: Businesses can visualize their strategic goals and align resources accordingly.
- Content Creation: Authors and marketers can brainstorm topics and Artikel content hierarchically.
Implementing mind mapping techniques in these areas allows individuals and teams to tap into their full potential, making it an indispensable tool for both personal and professional growth.
Closure
In summary, mind mapping serves as a versatile and powerful tool for plotting your next big idea, enabling you to visualize thoughts and streamline the creative process. By adopting the techniques discussed, individuals can avoid common pitfalls and maximize the potential of their ideas. As we have seen, the real-life applications of mind mapping extend across various industries, providing a framework for innovation and clarity in any endeavor.