How to Use Active vs. Passive Voice for Maximum Impact is a pivotal exploration into the nuances of voice in writing, essential for anyone looking to enhance their communication skills. Understanding the distinctions between active and passive voice can significantly influence how messages are conveyed and received, shaping the clarity and engagement of a text. This guide delves into the practical applications and implications of choosing the right voice, providing insights that can elevate your writing to new heights.
By dissecting the characteristics of both voices, we aim to equip you with the knowledge and techniques to master their use effectively. Whether you are crafting a compelling narrative or writing a technical report, knowing when to employ active or passive voice can make a crucial difference in your audience’s perception and response.
Understanding Active and Passive Voice
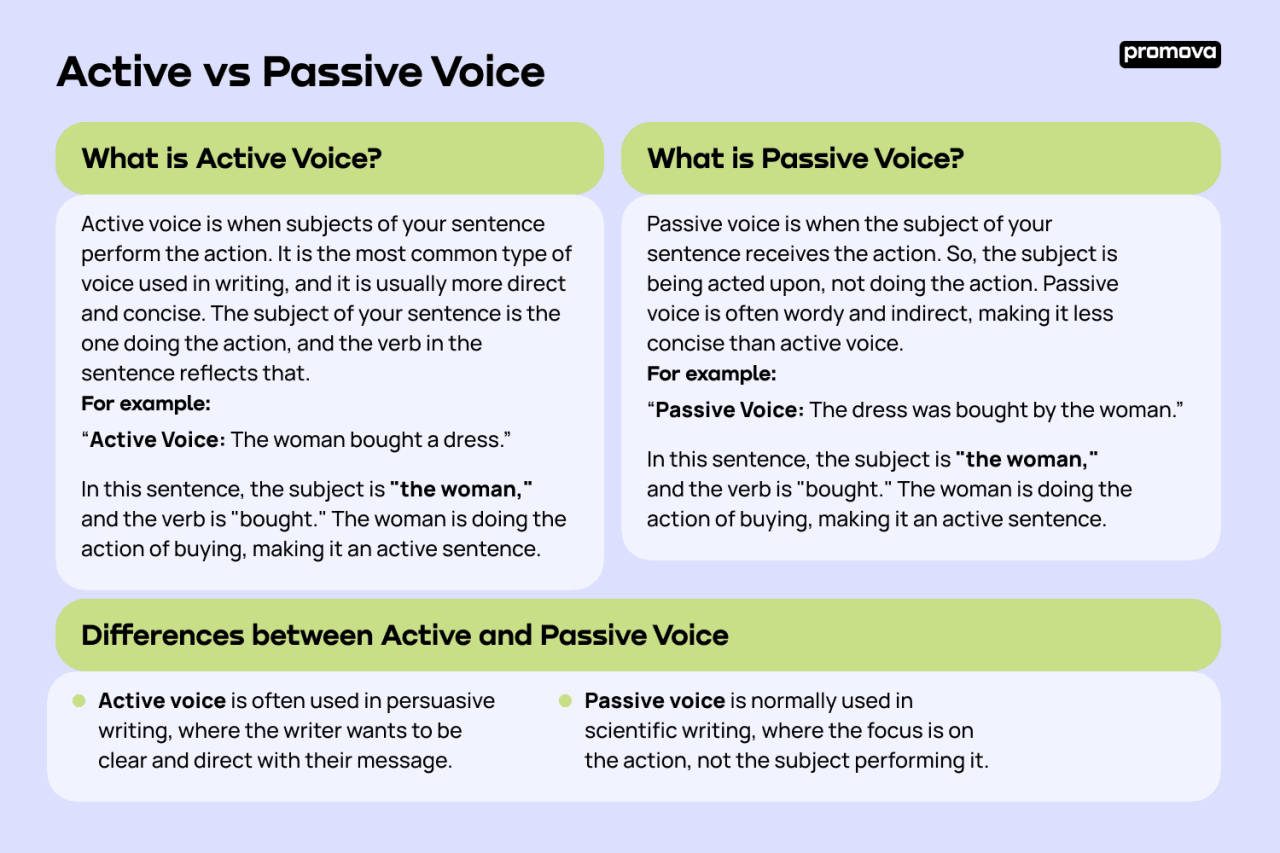
Active and passive voice are crucial concepts in writing that significantly influence clarity and engagement. The distinction between the two voices lies in the structure of the sentence and the focus of the action. Understanding these differences enables writers to convey their messages effectively and to tailor their communication style based on the desired impact.Active voice occurs when the subject of the sentence performs the action, making it straightforward and dynamic.
In this structure, the sentence typically follows a clear pattern: subject, verb, and object. For example, in the sentence “The chef cooked the meal,” the chef (subject) is actively performing the action of cooking (verb) the meal (object). This construction promotes clarity and often creates a more engaging reading experience.In contrast, passive voice occurs when the subject of the sentence is acted upon by the verb.
The structure typically follows this order: object, verb, and subject. For example, “The meal was cooked by the chef” illustrates this form, where the meal (object) is the focus, rather than the chef (subject) performing the action. While passive voice can be useful in emphasizing the action or the recipient of the action, it may lead to ambiguity or weak sentence construction if overused.The choice between active and passive voice significantly impacts writing style and effectiveness.
Using active voice tends to enhance clarity and directness, allowing readers to easily grasp the main points. Conversely, passive voice may benefit formal writing or scientific contexts where the focus is on the process or result rather than the individual performing the action. Understanding when to employ each voice will empower writers to create more compelling and persuasive content.
Characteristics of Active Voice
Active voice is characterized by its straightforward structure and clarity. The focus is on the subject performing the action, which typically results in more vigorous and immediate writing. Key attributes of active voice include:
- Clarity: The subject performs the action, reducing ambiguity and enhancing understanding.
- Engagement: Active constructions tend to create a more dynamic reading experience.
- Directness: The straightforward structure allows for quick comprehension of the main idea.
Incorporating active voice in writing can elevate the overall quality and impact of the message. For instance, “The team developed the project ahead of schedule” clearly states who is responsible for the action and emphasizes their achievement.
Characteristics of Passive Voice
Passive voice has distinct features that set it apart from active voice, particularly its emphasis on the action or the recipient of the action rather than the doer. The main characteristics include:
- Focus on the action: The action itself takes precedence, which can be useful in contexts where the agent is less important.
- Less direct: Passive constructions can create distance between the action and the subject, sometimes leading to ambiguity.
- Formal tone: Often found in academic or formal writing, where the process or results are prioritized over the individual.
An example of passive voice would be, “The project was completed by the team,” where the focus is on the project rather than who completed it. This can be particularly effective in research papers, where the results are more significant than the researchers.
The choice between active and passive voice shapes the clarity and impact of your writing.
When to Use Active Voice
Active voice is a powerful tool in writing that emphasizes clarity and directness. It places the subject of a sentence at the forefront, making the action more immediate and engaging for the reader. Understanding when to utilize active voice can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your communication.Active voice is most effective in scenarios where clarity and engagement are paramount. This includes persuasive writing, storytelling, and any context where concise communication is essential.
By prioritizing the subject-verb-object structure, writers can ensure their message is delivered with impact and vigor.
Scenarios for Effective Active Voice Usage
There are various situations where employing active voice can markedly improve the quality of writing. Below are key contexts in which active voice should be the preferred choice:
Persuasive Writing
In advertisements and opinion pieces, active voice makes arguments more compelling. For example, “The company launched a new product” is more forceful than “A new product was launched by the company.”
Narrative Storytelling
In creative writing, active voice helps to create vivid imagery and dynamic pacing. Consider the sentence “The children played in the park,” which paints a lively scene compared to “The park was played in by the children.”
Instructional Materials
When presenting guidelines or procedures, active voice clarifies steps. For instance, “Mix the ingredients thoroughly” is clearer than “The ingredients should be mixed thoroughly.”
Reports and Presentations
In professional contexts, active voice enhances clarity in data presentation. For instance, “The team completed the project ahead of schedule” directly conveys achievement, unlike “The project was completed ahead of schedule by the team.”Active voice not only clarifies the subject’s role in the action but also fosters a stronger connection with the audience.
Utilizing active voice enhances clarity, engagement, and urgency in writing, making it an essential choice for effective communication.
When to Use Passive Voice

The passive voice serves a distinct purpose in writing, particularly in situations where the focus shifts from the subject performing an action to the action itself or the recipient of the action. Understanding when to employ passive voice is essential for effective communication, particularly in formal contexts where the agent may be unknown or irrelevant.Passive voice is appropriate in several contexts, including instances where the doer of the action is less important than the action itself, or when the doer is unknown or unintentional.
The following examples illustrate the effectiveness of passive voice in various situations:
-
The cake was eaten.
-In this case, the focus is on the cake rather than who ate it.
-
The report was completed ahead of schedule.
-This emphasizes the completion of the report rather than the individual who completed it.
-
Mistakes were made during the experiment.
-Here, the mistakes are highlighted without attributing blame to a specific person.
Role of Passive Voice in Scientific and Technical Writing
In scientific and technical writing, the passive voice plays a crucial role in maintaining objectivity and neutrality. By emphasizing the action or process rather than the individual conducting the research, writers can present information in a more impartial manner. This is particularly important in research reports, academic articles, and technical documentation where the integrity of data and findings is paramount.An example of passive voice in scientific writing is as follows:
The results were analyzed using advanced statistical methods.
This phrasing highlights the analysis process, contributing to a clearer understanding of the methods applied without diverting attention to the researchers involved. Furthermore, passive constructions can also aid in the clarity of procedural descriptions. For instance:
The solution was heated to 100 degrees Celsius.
This sentence directs focus to the procedure rather than the individual who performed it, which is essential for replicability in scientific studies.In summary, passive voice is a valuable tool in both formal and scientific writing contexts. By shifting the focus from the actor to the action or outcome, writers can enhance clarity, objectivity, and focus on the pertinent information at hand.
Impact on Reader Perception
The choice between active and passive voice significantly influences how readers engage with a text. Understanding this impact is essential for effective communication, as the voice employed shapes not only clarity but also reader emotions and perceptions. Active voice often leads to a more immersive reading experience, while passive voice can introduce ambiguity and distance.Active voice tends to create a sense of immediacy and engagement for readers.
When a sentence is structured in active voice, the subject performs the action, which generally leads to clearer and more dynamic writing. This clarity can draw readers in, making them feel more connected to the narrative or argument presented. In contrast, passive voice often places the focus on the action itself and can obscure the subject, resulting in a more detached and sometimes vague reading experience.
Emotional Impact of Active vs. Passive Voice
The emotional impact of the voice used in writing can be profound. Active voice conveys action and decisiveness, often eliciting stronger emotional responses from readers. For example, a statement like “The storm destroyed the town” is immediate and evokes a sense of urgency and devastation. Conversely, the passive construction “The town was destroyed by the storm” introduces a layer of separation that may diminish the emotional resonance of the event.
By relying heavily on passive voice, writers may inadvertently neutralize the intensity of the message, affecting how it is perceived by the audience.In addition, the emotional weight of narratives can shift based on voice choice. Active voice imbues sentences with energy and passion, fostering an engaging atmosphere. This is particularly important in persuasive writing or storytelling, where capturing the reader’s emotions is essential for effectiveness.
Passive voice, while useful in certain contexts, can lead to a tone that feels flat or impersonal. Writers should therefore carefully consider their voice choices to maintain the desired emotional tone throughout their work.
Altering Tone and Mood through Voice Choice
The tone and mood of a piece are heavily influenced by whether active or passive voice is used. Active voice tends to create a lively and assertive tone, promoting clarity and directness. This is particularly effective in instructional writing, speeches, and other contexts where clear guidance is paramount. For instance, “The team will launch the project next week” offers a confident and forward-looking tone that can inspire action and optimism.In contrast, passive voice often contributes to a more formal or academic tone, which may be suitable for specific contexts such as technical writing or scientific reports.
However, this formality can sometimes lead to a sense of aloofness or detachment. For example, “The project will be launched next week” conveys the same information but lacks the immediacy of the active construction. Writers must weigh the desired tone against the audience’s needs to ensure that their message is not only clear but also appropriately impactful.The choice of voice is therefore a critical element in crafting effective communication.
Both active and passive constructions have their place, but understanding their effects on reader perception can enhance the overall impact of a written piece.
Techniques for Mastering Voice
Understanding the distinction between active and passive voice is crucial for effective writing. Mastering voice can enhance clarity, engagement, and overall impact on your readers. This section provides a structured approach to converting passive sentences to active voice, tips for recognizing voice during editing, and a checklist to evaluate voice usage in your writing.
Step-by-Step Method for Converting Passive Sentences to Active Voice
Converting passive sentences to active voice involves a systematic approach that can significantly enhance the dynamism of your writing. Follow these steps:
- Identify the verb in the passive sentence.
- Determine the subject of the action, which is often the object in the passive construction.
- Reconstruct the sentence by placing the subject first, followed by the verb and then the object.
- Adjust any additional elements in the sentence to ensure grammatical correctness.
For example, the passive sentence “The book was read by Sarah” transforms into the active voice as “Sarah read the book.”
Tips for Identifying Voice in Your Writing During the Editing Process
Being able to identify voice in your writing is essential for effective editing. The following tips can help you discern whether your sentences are in active or passive voice:
Pay attention to the structure: active voice typically follows a clear subject-verb-object format.
- Look for forms of the verb “to be” (is, are, was, were) which often indicate passive voice.
- Check for the presence of a “by” phrase, as this often suggests a passive construction.
- Read your sentences aloud; active voice tends to sound more engaging and direct.
- Analyze the focus of each sentence: determine who is performing the action versus who is receiving it.
Checklist to Evaluate Voice Usage in Your Writing
A checklist can be an effective tool to evaluate and refine your use of voice in writing. Consider the following criteria to assess your work:
Ensure that your writing reflects clarity and directness through active voice.
- Is the subject performing the action in most sentences?
- Are passive constructions limited to instances where emphasis on the action or receiver is necessary?
- Does the use of active voice enhance the overall readability of the text?
- Have I varied my sentence structure to maintain reader interest?
- Are any passive sentences revised for greater impact in conveying the message?
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Writers often encounter several pitfalls when navigating the use of active and passive voice. These mistakes can undermine clarity and reduce the overall impact of their writing. By identifying and addressing these common errors, writers can enhance their communication and ensure their messages are effectively conveyed.One frequent mistake is an over-reliance on passive voice, which can lead to vague or convoluted sentences.
For example, the sentence “Mistakes were made” lacks clarity regarding who made those mistakes. A clearer revision would be “The team made mistakes,” directly attributing the action to the responsible party. This revision exemplifies how active voice can enhance clarity and engagement.
Frequent Pitfalls in Sentence Construction
Writers may also fall into the trap of mixing active and passive constructions ineffectively. This inconsistency can confuse readers. Below are examples of such pitfalls, along with suggested revisions:
-
Original: “The project was completed by the students after much effort.”
Revision: “The students completed the project after much effort.” -
Original: “The research was conducted by the scientists, and the findings were published.”
Revision: “The scientists conducted the research and published the findings.” -
Original: “A decision was made to change the strategy by the management.”
Revision: “Management made a decision to change the strategy.”
Each of these examples illustrates how passive voice can obscure the subject and action, making sentences less direct and impactful. Maintaining a balance between active and passive voice is crucial for clarity. While active voice generally provides stronger, more direct sentences, passive voice can be valuable in certain contexts, particularly when the actor is unknown or irrelevant. Writers should be mindful of this balance, ensuring that passive structures serve a purpose rather than detracting from the main message.
“Effective writing combines the strengths of both active and passive voice, utilizing each where its strengths can shine.”
In summary, avoiding common mistakes and maintaining clarity through careful voice selection can significantly enhance the impact of writing. By being aware of these pitfalls and revising sentences for clarity and directness, writers can more effectively engage their audience.
Practical Applications in Different Writing Styles

In the realm of writing, the choice between active and passive voice can significantly shape the reader’s engagement and comprehension. This variation is especially pronounced across different genres, such as fiction, non-fiction, and academic writing. Understanding how voice influences each of these styles is crucial for effective communication and audience connection.In fiction, active voice often drives the narrative forward with immediacy and energy.
For instance, “The detective solved the mystery” places the protagonist at the forefront of the action. In contrast, passive voice can create suspense or highlight the impact of actions on characters, as in “The mystery was solved by the detective.” This choice can subtly alter the reader’s perception of the story’s dynamics and character motivations.In non-fiction writing, clarity and directness are typically prioritized, making active voice the preferred choice.
For example, “The study demonstrates a significant correlation” effectively conveys information. However, passive voice can be useful when the focus needs to shift from the doer to the action itself, as in “A significant correlation was demonstrated in the study.” This approach may be utilized in reporting or when the author wishes to maintain a neutral tone.Academic writing often adheres to specific conventions that dictate voice usage.
Active voice is favored for its clarity and assertiveness, as in “Researchers found a link between diet and health outcomes.” Yet, passive voice is not uncommon, particularly when the research process or results are emphasized, such as in “The link between diet and health outcomes was found by researchers.” This duality reflects the desire for objectivity while also accommodating the nuances of research presentation.Different audiences respond to voice choices in distinct ways, which can influence the effectiveness of the writing.
Audience Response to Voice Choices
Understanding how various audiences perceive active and passive voice is essential for tailored communication. The following points Artikel typical responses based on writing style:
- Fiction Readers: Often prefer active voice for its vividness and emotional engagement. A dynamic narrative involving characters in action tends to resonate more deeply.
- Non-Fiction Audiences: Appreciate clarity and straightforwardness. Active voice conveys authority and confidence, leading to better retention of information.
- Academic Readers: Expect a blend of voices. While active voice is direct, passive constructions can lend an air of formality and impartiality, crucial for scholarly discourse.
Understanding audience expectations regarding voice can enhance the effectiveness of one’s writing across genres.
In conclusion, the choice of voice varies significantly across writing styles, with active voice generally promoting engagement and clarity, while passive voice can serve to create distance or emphasize actions over actors. By analyzing audience responses, writers can make informed decisions that align their voice with the purpose and style of their writing.
Exercises for Improvement
To enhance one’s command of active and passive voice, practical exercises can be invaluable. These activities not only refine writing skills but also develop an intuitive understanding of when to employ each voice effectively. Engaging in these exercises encourages critical thinking and reinforces the principles covered in earlier sections, ultimately leading to clearer and more impactful writing.
Practice Exercises for Active and Passive Voice
Incorporating varied exercises can significantly bolster one’s mastery of active and passive voice. Below are suggested practices that cater to different writing styles and contexts:
- Transform Sentences: Take ten sentences written in active voice and convert them into passive voice, and vice versa. This exercise helps in identifying structural differences and enhances flexibility in writing.
- Identify the Voice: Read a selected passage from a published work and underline instances of active and passive voice. Analyze how the choice of voice affects the tone and clarity of the text.
- Rewrite for Effect: Choose a paragraph from your own writing and rewrite it first in active voice, then in passive voice. Reflect on which version conveys the intended message more powerfully.
- Create Sentences: Write five original sentences using active voice, then five using passive voice. Aim for variety in verb usage to explore the range of expressions possible within each voice.
Guidelines for Peer Review Focused on Voice Effectiveness
Peer reviews can provide beneficial insights into how effectively one employs active and passive voice. Establishing clear guidelines for this review process can enhance feedback quality, leading to improved writing.
- Clarity and Engagement: Evaluate how effectively the writer engages the reader. Does the active voice create a sense of immediacy and action, while passive voice might obscure the subject’s role?
- Consistency: Check for consistency in voice throughout the piece. Mixed voices can confuse the reader and dilute the message being conveyed.
- Intentional Use: Assess whether the use of passive voice is intentional and adds value to the writing. Consider if it serves a specific purpose, such as emphasizing the action over the subject.
- Suggestions for Improvement: Provide constructive criticism and specific suggestions on how the writer can enhance voice effectiveness. Highlight areas where a shift between voices could improve clarity or impact.
Benefits of Reading Aloud to Assess Voice in Writing
Reading aloud is a powerful technique that allows writers to hear the flow and rhythm of their words, providing critical insight into the effectiveness of voice usage. This practice offers several advantages:
- Auditory Feedback: Hearing the text spoken can reveal awkward phrasing and areas where the voice may falter. Writers can identify sentences that feel cumbersome or unnecessarily complex.
- Emphasis on Tone: Reading aloud allows writers to gauge the tone of their writing. Active voice typically conveys a more dynamic tone, while passive voice may introduce a shift in emphasis that could affect reader perception.
- Identification of Patterns: This exercise can help in recognizing patterns in voice usage, allowing writers to evaluate whether their writing maintains a consistent voice throughout.
- Enhanced Editing: Many writers find that hearing their work can lead to more effective editing, as they are more likely to catch errors or misused voice that might be overlooked when reading silently.
Ultimate Conclusion

In conclusion, understanding how to navigate the realms of active and passive voice is vital for achieving maximum impact in your writing. By recognizing the appropriate contexts for each voice and applying the techniques discussed, you can enhance the clarity, engagement, and emotional resonance of your work. Embracing these strategies will not only improve your writing but also deepen your connection with your audience, leading to more effective communication overall.